Taints and Tolerations
Taints and Tolerations are used in Kubernetes to mark single Nodes for specific use-cases (taints) and allowing pods to be scheduled on such Nodes (tolerations).
Adding Taints via the Dashboard
In the creation step for a Node Deployment we provide settings that all Nodes of this Node Deployment are created with Labels and/or Taints:
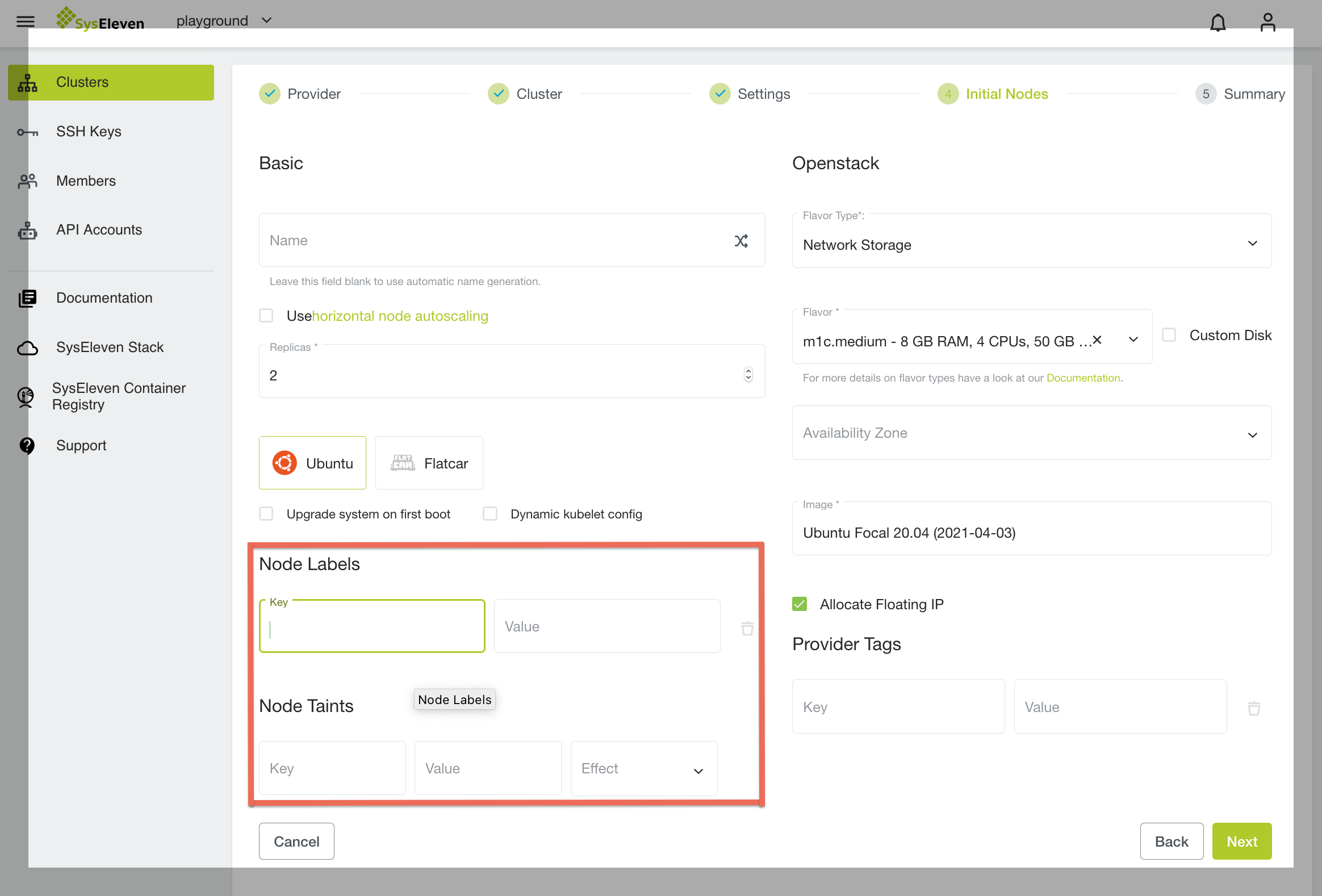
Newly created machines will then automatically be tainted and/or labelled with the values you chose. In a typical setup one would set a Taint with NoSchedule Effect and a matching label on the Node (e.g. Key dedicated and Value web).
You can also update existing Node Deployments, but be aware, that all Nodes of that Node Deployment will then be recreated.
Adding Taints via CLI
While it is possible to taint single Nodes manually over the Kubernetes API with kubectl we do not recommend to do so when using your MetaKube cluster, since each update of the Nodes will recreate them and they will loose their taints.
Instead you should add the taints and labels directly to the MachineDeployments in your cluster. You can edit the resources with kubectl:
kubectl edit machinedeployment <name> --namespace kube-systemAnd then add or edit the .spec.template.spec.metadata.labels and .spec.template.spec.taints fields:
apiVersion: cluster.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: MachineDeployment
spec:
[...]
template:
[...]
spec:
metadata:
name: <name>
labels:
dedicated: web
[...]
taints:
- effect: NoSchedule
key: dedicated
value: web
[...]Please be aware that your machines will be recreated when you edit the MachineDeployment.
Adding Tolerations
Pods which shall run on dedicated Nodes then need two settings: The toleration to be allowed to be scheduled on these Nodes and a NodeSelector to be restricted to only these Nodes. When creating the pods with a Deployment, you need to add both settings in the PodSpec of the Deployment (e.g. Key dedicated and Value web):
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: web
spec:
[...]
template:
[...]
spec:
tolerations:
- operator: Equal
effect: NoSchedule
key: dedicated
value: web
[...]
nodeSelector:
dedicated: web
[...]If you require more complex selection of Nodes you can use a NodeAffinity rule instead of a NodeSelector, which greatly expands the type of constraints for the Node selection.